Table of Contents
1. What is Personalisation in Banking?
2. Benefits of Personalisation in Banking
3. What are the Technologies Supporting Personalisation in Banking?
4. What are the Use Cases for Personalisation in Banking?
5. How to Implement Personalisation Effectively?
6. What is the Future of Personalisation in Banking?
1. What is Personalisation in Banking?
Personalisation, can be defined as “the action of designing or producing something to meet someone’s individual needs.”
Regardless of the industry or business type a certain level of personalisation (ie. meeting individual’s needs) has become a standard approach to interacting with customers and has changed the type of experience consumers expect to receive.
We are in the era of personalised digital services like Netflix, Google and Amazon who have created value for themselves and their customers by using data and personalisation as a core part of their service offering.
When it comes to banking, similarly to other industries, customers are expecting more. The move away from in-branch banking to digital-only banking is becoming a reality and while the majority of customers are happy to move online that does not mean they are happy to sacrifice the personalised experiences they get from a face-to-face interaction.
Personalisation can be a competitive advantage for banks and can serve as a way to increase customer loyalty. When used correctly it can deliver more effective marketing campaigns and engage customers in new ways.
However, the true promise of personalisation in banking is to go beyond just marketing campaigns and to focus on understanding customer needs at the individual level and using this knowledge to transform all customer interactions. It is through this transformation that banks can really build deep and long-lasting relationships with customers. Research from Gartner shows that brands that provide help to customers across personalisation experiences, opposed to just personalised marketing, are likely to see a 16% lift in commercial benefit.
Compared to other industries banks have access to far greater levels of customer data and so are in a position to radically change the way they interact with their customers and to deliver exceptional customer experiences.
2. What are the Benefits of Personalisation in Banking?
- Improved Loyalty
Personalisation creates a deeper relationship between bank and customer where the customer trusts their bank and recognises the value of the products services and advice being provided to them. These valuable interactions and strong relationships will lead to improved loyalty amongst customers.
- Increased Engagement
By understanding the individual needs of customers, banks can create experiences that are more compelling and engaging. Shifting the mindset from product-push to personalised notifications based on needs can improve customer satisfaction and drastically increase engagement.
The more time customers spend in bank apps, the more exposure they have to the bank brand which will keep it top of mind when deciding on future banking products and services.
- Competitive Advantage
Banks are under increased pressure from new entrants to upgrade the experiences they offer to customers. In order to not only keep up with new entrants but also to gain advantage banks need to incorporate a level of personalisation in all of their customer interactions.
- Marketing Effectiveness
A typical use-case for personalisation is to improve the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. When banks understand what an individual customer needs they can create and promote products and services that fit a customers unique set of requirements.
3. What are the Technologies Supporting Personalisation in Banking?
The move towards personalised digital banking has been made possible by smartphones and the shift in consumer preference for online banking. These factors along with a number of modern technologies have made it possible for banks to provide personalised experiences to customers.
- Artificial Intelligence
The term Artificial Intelligence (AI), as used in business environments today, encompasses a range of technology and approaches, including Machine Learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP).
AI makes it possible for banks to learn more about customer behaviours, and provides the tools to anticipate their needs, identify opportunities and improve the service provided to them.
- Data Analytics
Data has always played an integral role in the banking system. From assessing risk to managing day-to-day lending to monitoring transactions.
Today, thanks to smartphones and the move of customers online, banks now have access to huge amounts of detailed data that go beyond the basic demographic data.. Data analytics technology has made it possible for banks to analyse, categorise and make sense of all of this data which makes it possible to provide personalised notifications and recommendations to customers.
- APIs
Application Programming Interfaces or APIs are a group of tools or protocols that are used to create and share banking products and services. They allow third parties to connect to a bank or financial service provider and access its common tools, services and valuable assets, such as financial information, customer accounts and product catalogues.
By connecting to third-parties who may be specialised in data analytics or personalisation, banks can swiftly introduce personalised experiences.
4. What are the Use Cases for Personalisation in Banking?
There are many benefits of personalising customer experiences but what are some of the most important areas where personalisation can have a big impact on the customer-bank relationship.
- Personal Financial Management (PFM)
Technology has made it possible for banks to provide digital tools that customers can access to better manage their finances. Personal Financial Management or PFM encompasses any recommendations, insights or nudges that help customers to manage their finances in an educated and transparent way.
Personalised financial management tips and insights can encourage customers to create budgets, set-up savings goals and even predict future financial situations.
- Financial Literacy & Advisory
Financial literacy is the ability to understand and effectively use financial skills to manage finances and can include having knowledge of budgeting, investing and lending, areas that customers commonly struggle to manage effectively.
Not all financial education is relevant to every customer but thanks to personalisation, banks can target customers with the educational that they need and that will help them the most.
- Card-linked Offers
Card-linked offers are a digital tool used to bridge the gap between in-app / online activities with real-world experiences.
Card-linked offers can can drive mutually beneficial relationships between banks, merchants and customers by improving loyalty, increasing card spend and therefore driving customer engagement.
Personalisation allows banks to segment customers effectively and to target them with relevant card-linked offers. For customers, these offers can help them to cut back on spending and save money.
- Contextual Marketing
Contextual marketing in banking connects customers with offers and updates in the right place and at the right time.
Banks can analyse and categorise customers transaction data and gain insights into their previous behaviours and actions. With this information banks can market personalised products and services that customers actually need, want and can afford. This increases the levels of engagement with customers and improves their satisfaction with the marketing content they are being shown.
5. How to Implement Personalisation Effectively?
While the benefits are obvious and the implementation possible, data-driven personalisation still comes with its challenges. It is a fine balancing act between embracing data analytics, behavioural science and respecting customer preferences, which can be difficult.
When you focus too much on the technology and forget about the customers and their behaviours, you can run into problems implementing effective personalisation strategies. The customer must be at the centre of personalisation initiatives and financial institutions (and fintechs) must not get carried away with data analytics, machine learning models and technology at the expense of a meaningful experience for the end user. In order to implement data-driven personalisation effectively we recommend using the following checklist:
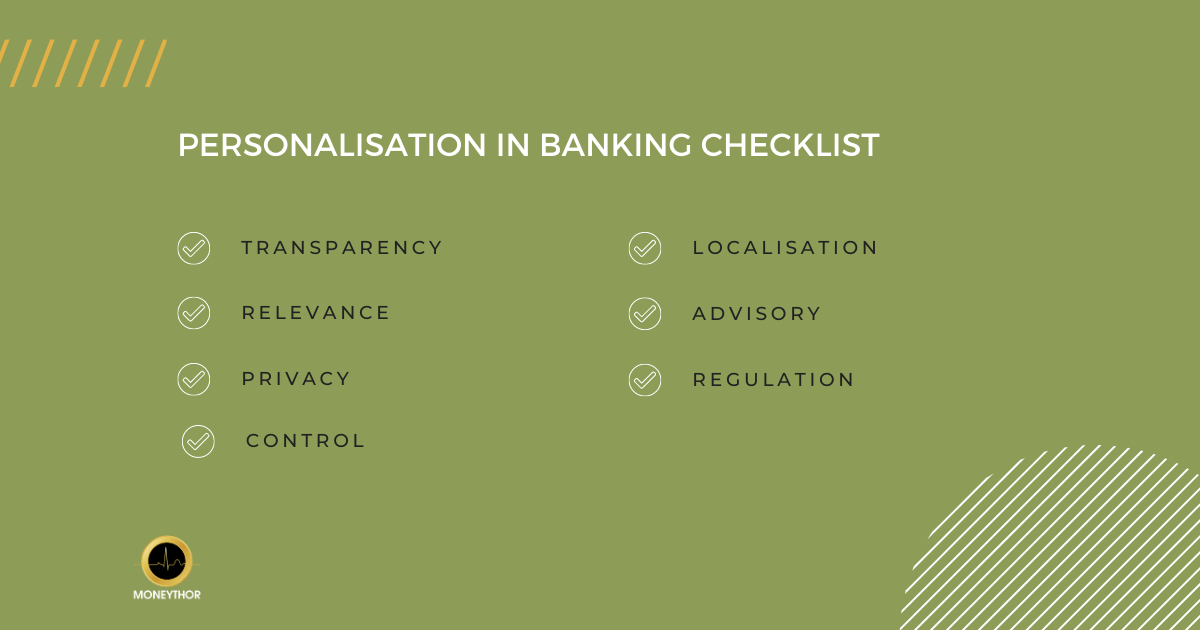
- Transparency
Consumers and businesses want to have better digital banking experience and are happy for their data to be used to get it, but only if they have visibility over how this data is being used.
Without context and background, personalised content can seem out of place even if technically true according to your underlying machine learning model. By being transparent with the data used to power notifications and alerts, financial institutions can not only build confidence and trust amongst their customers, but it will lead to higher engagement as customers will interact more with a notification when they understand why they are being shown it.
- Relevance
All customers are unique. Their spending and saving habits are different as are the ways they interact with financial institutions. Customers want to know that you understand their individual needs and wants and by showing them relevant content you can do just that. When used intelligently, data allows banks and fintech firms to create unique contextual experiences which can grab and hold a user’s attention, generating engagement and loyalty towards a financial brand.
- Privacy
Customers expect curated experiences which are personalised and valuable, while at the same time they are increasingly skeptical about how their data is being used and cautious about giving it away. There is a fine line between knowing about your customers and being creepy or making them feel as though you are spying on them. 57% of consumers say they will unsubscribe, and 38% will stop doing business with a brand in response to perceived creepiness.
Respecting privacy both in the eyes of regulators and the customer are key to making customers satisfied with how their data is being used while enhancing the user experience.
- Control
Customers should feel like at every point that they have the choice and control to decide how their experience is personalised.
Engage in feedback with them and let them decide what content they enjoy seeing and what content they don’t. Establishing feedback loops gives customers control over their experience and helps financial institutions figure out which content works, and which content doesn’t.
- Localisation
Delivering the right message at the right time and right place is a must for personalisation strategies. Adapting the content shown to customers depending on their language, cultural affinity and location is key for nailing strong experiences, even those involving contextual marketing or promoting merchant offers.
- Advisory
The way content is framed, and the tone of voice being used will impact how effective the content is. The content which appears within banking channels is expected to add intrinsic value to the way customers manage their finances, such as advising them on whether or not to make a purchase. Using personalisation exclusively for cold marketing content won’t perform as well and will eventually lead to frustrated customers.
- Regulation
While this may seem obvious, when it comes to using data analytics, personalisation and nudging, it is important that any initiatives which are implemented are within the boundaries of any local regulatory framework, so be sure you are following the regulations set out in your relevant geographies. A particular item to pay attention to is what is deemed “financial advice” in the local jurisdiction.
6. What is the Future of Personalisation in Banking?
The move towards digital-only banking has transformed how customers manage their finances and how banks serve their customers. Personalisation will play a key role in this transformation. But what does the future for personalisation in banking look like?
The future of banking and technological progress are, and will continue to be, intrinsically linked. As technologies like AI and data analytics continue to advance and become more established, the banking experience will too transform.
This transformation will need to be in keeping with consumers ever growing needs and expectations. The proliferation of smartphones increases every year and as 5G internet access becomes the norm, the level of service expected digitally will drive the increased need for personalisation online.
The need for personalised services will also be spurred on by the increased competition in the banking industry. Data and personalisation will become a differentiating factor in crowded banking markets and those banks that use data and AI most effectively to reimagine customer journeys will be best-positioned to beat out the competition.
At a national level, governments and regulatory bodies are keen to increase the levels of competition in markets and to ensure that customers are provided with an effective way of managing their financial situation. Regulation like Open Banking, is changing how data is provided to customers and how personalised a digital banking experience can be.
When it comes to the future of personalisation in banking, there is no doubt that it will play a key role. Technology and regulation are supporting its adoption and customer expectations are increasing at the same time.
Personalisation has the potential to disrupt the entire user experience with financial institutions, transforming relationships between customers and their banks from purely transactional to relational, helping banks to stay relevant and increase digital engagement.
Download Personalisation in Banking Guide
"*" indicates required fields


