What is Banking-as-a-Service?
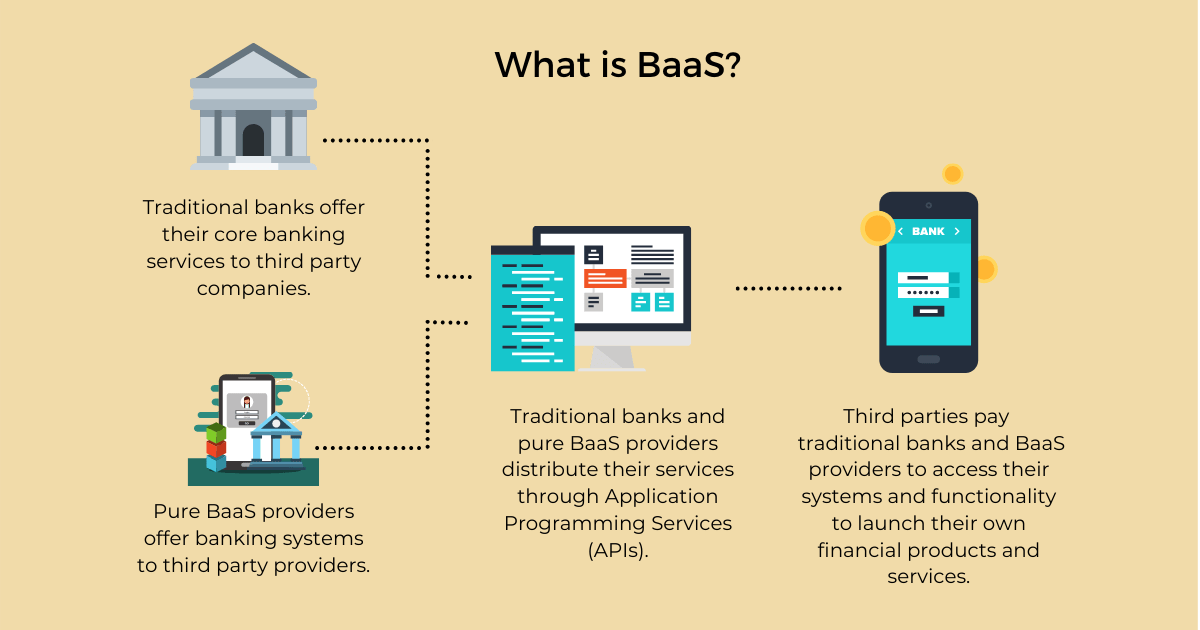
Banking-as-a-service (BaaS) is an end-to-end process where third parties – finTech, non-finTech, developers, etc. – can access and execute financial services capabilities without having to develop them organically.
BaaS involves players such as incumbent financial institutions and service providers , granting third parties such as fintechs access to core systems, functionality and licensing so that they can integrate digital banking and payment services into their own products.
Facilitated by Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), third parties can build banking offerings on top of the providers’ regulated infrastructure with ease and efficiency saving them time and money while creating new revenue streams for traditional players.
What are the factors driving the adoption of BaaS?
BaaS has emerged as a new and innovative way for banks and third parties to collaborate in order to provide customers with digital-only banking products and services and enhanced customer experiences.
Over the last number of years BaaS has become a mainstay in the financial services space. Digital-only banks powered by BaaS continue to launch and dedicated, “pure” BaaS service providers have emerged, creating a whole new banking sector. But what are the factors that have caused this rapid adoption of BaaS?
- Digital transformation
Traditional banking models have been turned on their heads as customers continue to adopt a mobile-first approach to banking and the need for digital-only banking services continues to grow.
The scale and resources required to transform traditional banks so that they can effectively serve modern, digital-only customers is a big undertaking and one that cannot be achieved alone. Incumbent banks cannot provide customers with the always-on, digital experience that they have come to expect without working with other financial services players.
It is with this in mind that incumbent banks have begun to shift towards a more open way of doing business and are embracing collaboration with would-be, potential competitors.
Incumbent banks are choosing to collaborate with emerging new players in order to develop new revenue streams.
- Innovative new players
It has never been easy for new players to enter the financial services industry. Regulatory requirements and steep set-up costs have not only deterred new entrants but slowed innovation in the sector.
Third party providers have had to look for more innovative ways of gaining access to the technology, regulatory approval and customer bases they need. Thanks to the BaaS model new entrants have been able to access the services and systems they need in half the time and without the monumental costs.
- API
Application programming interfaces (APIs) are key building blocks of digital banking and are reframing opportunity within financial services. APIs have helped incumbent banks and third parties to realise their business vision, build connected business models, and deliver innovative banking products and services. Without the industry-wide acceptance of APIs, BaaS would not be possible. The widespread adoption of APIs has been a key driving force in the development of BaaS.
What are the benefits of BaaS?
BaaS has caused a shift in the way that banks and third parties work together and has huge advantages for both the incumbent players and those starting out in the financial services industry.
Benefits for incumbent banks
New revenue streams
Banks need to navigate more competitive markets and find ways to drive profits while keeping costs low. Creating a BaaS platform and allowing third-party providers to access it for a fee can inject fresh revenue into the bank. Revenue models include recurring fees, setup charges or revenue sharing agreements.
Relevance in the digital age
New digital-only players have entered the banking space and thanks to lower fees and improved customer experiences are becoming popular with existing banking customers, reducing the need to keep a bank account with a traditional bank.
Incumbent banks should look for innovative ways to maintain their footing as a key player in the industry. BaaS is an opportunity for incumbent banks to remain relevant in the banking space.
Benefits for third party providers
Faster speed to market
By accessing a bank’s functionality, third-party providers can bypass some big development hurdles and go to market much quicker than if they chose to build their own functionality from scratch.
Overcome regulatory complexities
One of the biggest obstacles for third-party providers’ intent on providing financial services products is dealing with complicated regulation and compliance. By partnering with banks, they can circumvent this by piggybacking onto the banks’ licensing agreement.
How has BaaS changed the banking industry?
- Increased competition
aaS has removed multiple barriers to entry for new players in the financial services space by providing a simple and affordable way to build a banking infrastructure. Thanks to this fintechs and challenger banks have begun to make inroads with the customers of traditional banks.
Competition is not only coming from within the financial services industry, new financial products and services are being launched by businesses that are not fintech companies or challenger banks. The range of companies offering financial products and services has expanded to telcos, internet companies and insurers. BaaS has made it possible for businesses from other industries to offer these products and services to their existing customer bases.
- Improved customer experiences
Increased competition has led to increased innovation in the banking space which in turn has led to improved digital experiences for customers. Customers have greater choice than ever before when it comes to what financial products and services they use.
Banking-as-a-Service and Open Banking
Open Banking and BaaS are terms that are often used interchangeably. This confusion tends to arise because they both use APIs to connect with third parties. However, they are two separate concepts that present different opportunities and challenges for banks and other players.
Data vs Functionality
Open Banking, which is a secure way for banks to share financial information such as account and card data with third party providers, has been implemented globally to revolutionise how consumers manage their finances. Thanks to this access to data via APIs third party providers can offer enhanced and highly personalised experiences to customers and customers are provided with a more detailed view of their financial situation.
BaaS is similar to Open Banking in that it grants access to third parties through open APIs. However in place of granting access to data of existing bank customers, BaaS offers access to bank functionality.
For example, Open Banking allows third parties to provide customers with all of their banking data and view it in new and interesting ways; while BaaS gives a provider, like a fintech company, the ability to build its own, differentiated experience for its customers, under its own brand, supported by the bank’s existing infrastructure and expertise.
What is the future of BaaS?
Banking-as-a-Service has become a powerful vehicle for innovation as companies across industry verticals, beyond simply digital banking and personal finance, are starting to offer financial products and services.
- Platform banking
Platform-based business models have taken hold in the digital economy and the concept is starting to emerge in banking. A banking platform establishes standards for third party developers to build products and services on behalf of bank customers while allowing the banks to deliver a unified banking experience. In this model banks would still own the end-to-end experience but would allow third parties to offer their products and services within their marketplace.
BaaS has highlighted the potential opportunities of collaboration between incumbent banks and third party players and has paved the way for platform-banking to emerge.
- All brands can be banks
BaaS has made it simple and efficient for non-financial businesses to embed financial services into their customer experience. By offering a simple way for other businesses to launch financial products and services, BaaS has made it possible for any business to become a “bank”.
Some big brands like Google, Amazon and Uber have begun to make moves into the finance space using a BaaS model. This is expected to continue as more businesses look to add a financial services offering to their portfolio.
Download BaaS Guide
"*" señala los campos obligatorios


